-40%
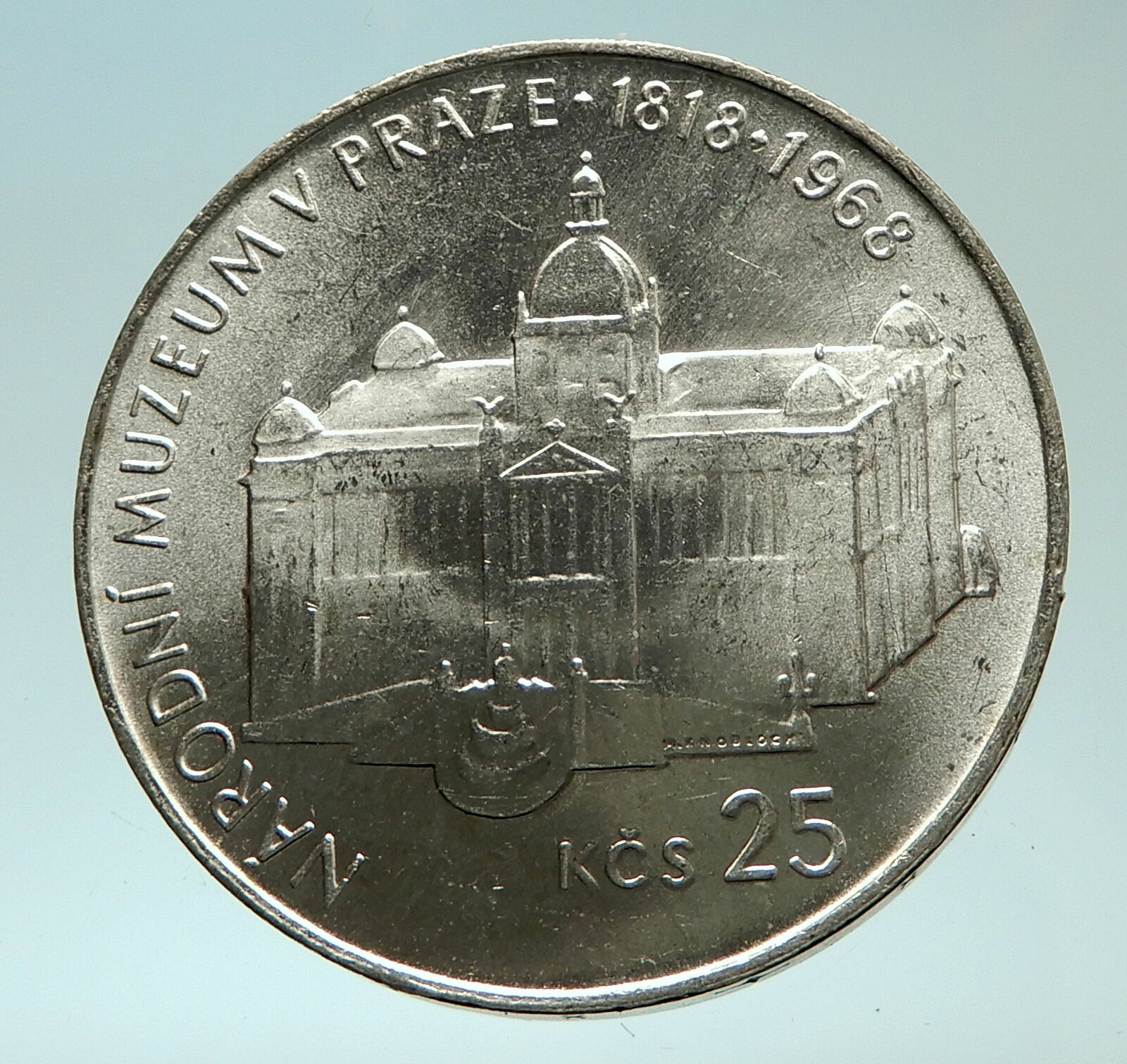
1968 CZECHOSLOVAKIA w Prague National Museum Genuine Silver 25 Korun Coin i75975
$ 89.57
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Item:i75975
Authentic Coin of:
Czechoslovakia - 150th Anniversary - Prague National Museum
1968
Silver 25 Korun 33mm (
16.05
grams) 0.500 Silver (0.2572 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 64
PATRIAE DECORI CIVIBUS EDUCANDIS ČESKOSLOVENSKÁ SOCIALISTICKÁ REPUBLIKA, Czech lion with socialist shield.
NÁRODNÍ MUZEUM V PRAZE 1819 . 1968 KČS 25 M.KNOBLOCH, National Museum Building.
Notes: After demonetization,1566 UNC and 108 Proof pieces were melted down.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
The
National Museum (NM)
(Czech:
Národní muzeum
) is a Czech museum institution intended to systematically establish, prepare and publicly exhibit natural scientific and historical collections. It was founded in 1818 by Kašpar Maria Šternberg. Historian František Palacký was also strongly involved.
At present the National Museum houses almost 14 million items from the area of natural history, history, arts, music and librarianship, located in dozens of buildings.
The founding of the National Museum should be seen in the context of the times, where after the French Revolution, royal and private collections of art, science, and culture were being made available to the public. The beginnings of the museum can be seen as far back as 1796, when the private Society of Patriotic Friends of the Arts was founded by Count Casper Sternberk-Manderschied and a group of other prominent nobles. The avowed purpose of the society was "the renewed promotion of art and taste", and during the time of Joseph II, it would be adamantly opposed to the King. In 1800 the group founded the Academy of Fine Arts, which would train students in progressive forms of art and history.
The National Museum in Prague
The National Museum in Prague was founded on April 15, 1818, with the first president of the Society of the Patriotic Museum being named Count Sternberk, who would serve as the trustee and operator of the museum. Early on, the focus of the museum was on natural sciences, partially because Count Sternberk was a botanist, mineralogist, and eminent phytopaleontologist, but also because of the natural science slant of the times, as perpetrated by Emperor Joseph II of Austria.
The museum was originally located in the Sternberg Palace but it was soon apparent that this was too small to hold the museum's collections. The museum relocated to the Nostitz Palace but this was also found to be of insufficient capacity, which led to the decision to construct a new building for the museum in Wenceslas Square.
The museum did not become interested in the acquisition of historical objects until the 1830s and 40s, when Romanticism became prevalent, and the institution of the museum was increasingly seen as a center for Czech nationalism. Serving as historian and secretary of the National Museum in 1841, Frantisek Palacky would try to balance natural science and history, as he described in his Treatise of 1841. It was a difficult task, however, and it would not be until nearly a century later until the National Museum's historical treasures equaled its collection of natural science artifacts.
However, the importance of the museum was not in its focus, but rather that it signaled, and indeed helped bring about, an intellectual shift in Prague. The Bohemian nobility had, until this time, been prominent, indeed dominant, both politically and fiscally in scholarly and scientific groups. However, the National Museum was created to serve all the inhabitants of the land, lifting the stranglehold the nobility had had on knowledge. This was further accelerated by the historian Frantisek Palacky, who in 1827 suggested that the museum publish separate journals in German and Czech. Previously, the vast majority of scholarly journals were written in German, but within a few years the German journal had ceased publication, while the Czech journal continued for more than a century.
In 1949, the national government took over the museum, and spelled out its role and leadership in the Museum and Galleries Act of 1959. In May 1964, the Museum was turned into an organization of five professionally autonomous components: the Museum of Natural Science, the Historical Museum, the Naprstek Museum of Asia, African, and American Cultures, the National Museum Library, the Central Office of Museology. A sixth autonomous unit, the Museum of Czech Music, was established in 1976.
Czechoslovakia
, or
Czecho-Slovakia
(/ˌtʃɛkoʊsloʊˈvækiə, -kə-, -slə-, -ˈvɑː-/; Czech and Slovak:
Československo
,
Česko-Slovensko
), was a sovereign state in Central Europe that existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until its peaceful dissolution into the Czech Republic and Slovakia on 1 January 1993.
From 1939 to 1945, following its forced division and partial incorporation into Nazi Germany, the state did not
de facto
exist but its government-in-exile continued to operate.
From 1948 to 1990, Czechoslovakia was part of the Eastern Bloc with a command economy. Its economic status was formalized in membership of Comecon from 1949 and its defense status in the Warsaw Pact of May 1955. A period of political liberalization in 1968, known as the Prague Spring, was forcibly ended when the Soviet Union, assisted by several other Warsaw Pact countries, invaded. In 1989, as Marxist-Leninist governments and communism were ending all over Europe, Czechoslovaks peacefully deposed their government in the Velvet Revolution; state price controls were removed after a period of preparation. In 1993, Czechoslovakia split into the two sovereign states of the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
Following Nazi Germany's surrender, some 2.9 million ethnic Germans were expelled from
Czechoslovakia
with Allied approval, their property and rights declared void by the Beneš decrees.
Czechoslovakia soon came to fall within the Soviet sphere of influence..
The popular enthusiasm evoked by the Soviet armies of liberation (which was decided by compromise of Allies and Joseph Stalin at the Yalta conference in 1944) benefited the KSČ. Czechoslovaks, bitterly disappointed by the West at the Munich Agreement (1938), responded favorably to both the KSČ and the Soviet alliance. Reunited into one state after the war, the Czechs and Slovaks set national elections for the spring of 1946.
The democratic elements, led by President Edvard Beneš, hoped the Soviet Union would allow Czechoslovakia the freedom to choose its own form of government and aspired to a Czechoslovakia that would act as a bridge between East and West. Communists secured strong representation in the popularly elected National Committees, the new organs of local administration. In the May 1946 election, the KSČ won most of the popular vote in the Czech part of the bi-ethnic country (40.17%), and the more or less anti-Communist Democratic Party won in Slovakia (62%).
In sum, however, the KSČ only won a plurality of 38 percent of the vote at countrywide level. Edvard Beneš continued as president of the republic, whereas the Communist leader Klement Gottwald became prime minister. Most importantly, although the communists held only a minority of portfolios, they were able to gain control over most of the key ministries (Ministry of the Interior, etc.)
Although the communist-led government initially intended to participate in the Marshall Plan, it was forced by the Kremlin to back out. In 1947, Stalin summoned Gottwald to Moscow; upon his return to Prague, the KSČ demonstrated a significant radicalization of its tactics. On 20 February 1948, the twelve non-communist ministers resigned, in part to induce Beneš to call for early elections; however Beneš refused to accept the cabinet resignations and did not call elections. In the meantime, the KSČ marshalled its forces for the Czechoslovak coup d'état of 1948. The communist-controlled Ministry of the Interior deployed police regiments to sensitive areas and equipped a workers' militia. On 25 February Beneš, perhaps fearing Soviet intervention, capitulated. He accepted the resignations of the dissident ministers and received a new cabinet list from Gottwald, thus completing the communist takeover under the cover of superficial legality.
On 10 March 1948, the moderate foreign minister of the government, Jan Masaryk, was found dead in suspicious circumstances that have still not been definitively proved to constitute either suicide or political assassination.
In February 1948, the Communists took power in the 1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état, and Edvard Beneš inaugurated a new cabinet led by Klement Gottwald. Czechoslovakia was declared a "people's democracy" (until 1960) - a preliminary step toward socialism and, ultimately, communism. Bureaucratic centralism under the direction of KSČ leadership was introduced. Dissident elements were purged from all levels of society, including the Roman Catholic Church. The ideological principles of Marxism-Leninism and socialist realism pervaded cultural and intellectual life.
The economy was committed to comprehensive central planning and the abolition of private ownership of capital. Czechoslovakia became a satellite state of the Soviet Union; it was a founding member of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (Comecon) in 1949 and of the Warsaw Pact in 1955. The attainment of Soviet-style command socialism became the government's avowed policy.
Slovak autonomy was constrained; the Communist Party of Slovakia (KSS) was reunited with the KSČ (Communist Party of Czechoslovakia), but retained its own identity. Following the Soviet example, Czechoslovakia began emphasizing the rapid development of heavy industry. Although Czechoslovakia's industrial growth of 170 percent between 1948 and 1957 was impressive, it was far exceeded by that of Japan (300 percent) and the Federal Republic of Germany (almost 300 percent) and more than equaled by Austria and Greece.
Beneš refused to sign the Communist Constitution of 1948 (the Ninth-of-May Constitution) and resigned from the presidency; he was succeeded by Klement Gottwald. Gottwald died in March 1953. He was succeeded by Antonín Zápotocký as president and by Antonín Novotný as head of the KSČ.
In June 1953, thousands of workers in Plzeň went on strike to demonstrate against a currency reform that was considered a move to solidify Soviet socialism in Czechoslovakia. The demonstrations ended without significant bloodshed, disappointing American Director of Central Intelligence Allen Dulles, who wished for a pretext to help the Czechoslovak people resist the Soviets. For more than a decade thereafter, the Czechoslovak communist political structure was characterized by the orthodoxy of the leadership of party chief Antonín Novotný, who became president in 1957 when Zápotocký died.
In the 1950s, the Stalinists accused their opponents of "conspiracy against the people's democratic order" and "high treason" in order to oust them from positions of power. In all, the Communist Party tried 14 of its former leaders in November 1952 and sentenced 11 to death. Large-scale arrests of Communists and socialists with an "international" background, i.e., those with a wartime connection with the West, veterans of the Spanish Civil War, Jews, and Slovak "bourgeois nationalists," were followed by show trials. The outcome of these trials, serving the communist propaganda, was often known in advance and the penalties were extremely heavy, such as in the case of Milada Horáková, who was sentenced to death together with Jan Buchal, Záviš Kalandra and Oldřich Pecl.
The 1960 Constitution declared the victory of socialism and proclaimed the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic (CSSR).
De-Stalinization had a late start in Czechoslovakia. In the early 1960s, the Czechoslovak economy became severely stagnant. The industrial growth rate was the lowest in Eastern Europe. As a result, in 1965, the party approved the New Economic Model, introducing free market elements into the economy. The KSČ "Theses" of December 1965 presented the party response to the call for political reform. Democratic centralism was redefined, placing a stronger emphasis on democracy. The leading role of the KSČ was reaffirmed, but limited. Slovaks pressed for federalization. On 5 January 1968, the KSČ Central Committee elected Alexander Dubček, a Slovak reformer, to replace Novotný as first secretary of the KSČ. On 22 March 1968, Novotný resigned from the presidency and was succeeded by General Ludvík Svoboda.
Frequently Asked Questionss
Mr. Ilya Zlobin
, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the "
Guide on How to Use My Store
" for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.